Understanding Rectifiers In Industrial Power Systems
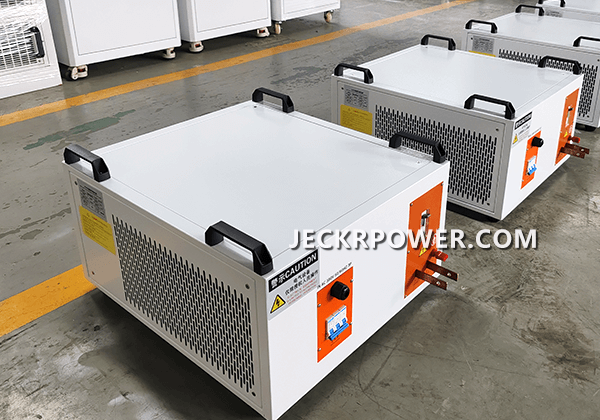
Rectifiers are key parts of electrical systems. They change alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC) to provide stable power. Industries like electroplating, anodizing, and micro-arc oxidation rely on rectifiers. These devices ensure smooth processes and high-quality results. But what exactly makes rectifiers indispensable for industries? Let’s look at what they do. We’ll see how they differ from other parts. We’ll also learn why they matter in the industry.
What is a rectifier? How does it work?
A rectifier changes AC into DC. This is important for industries needing steady power. AC flows in two directions. This does not work for electroplating or anodizing. Rectifiers use diodes or semiconductors to make the current flow in one direction.
In electroplating, a rectifier ensures a steady flow of current. This deposits an even layer of metal onto a surface. Likewise, in anodizing, rectifiers create a consistent oxide layer on metal surfaces. This ensures the durability and uniformity of the surface. Without rectifiers, these processes would face power instability, leading to subpar results.
Why are rectifiers important in industrial power supply?
Rectifiers are critical in industry. They ensure power systems run smoothly and reliably. Stable power is key for good results in electroplating, anodizing, and micro-arc oxidation (plasma electrolytic oxidation).
Take electroplating as an example. This process deposits a thin metal layer onto a substrate. It improves durability, corrosion resistance, and appearance. We need a steady DC power supply to create a uniform metal layer. If the power changes, the coating may become uneven. This could cause defects or a failure of the process. In anodizing, rectifiers keep the power steady. This helps create a strong and smooth oxide layer.
Rectifiers improve efficiency by providing a reliable power source. They also cut defects, saving time and costs.
What is the difference between a rectifier, transformer, regulator, and inverter?
Rectifiers, transformers, regulators, and inverters are important in electrical systems. But they serve different purposes depending on specific needs:
- Rectifier: It changes AC to DC. It is needed for electroplating, anodizing, and charging batteries.
- Transformer: This changes the voltage of AC. It does not change AC to DC. It ensures that devices receive the correct voltage.
- Regulator: Stabilizing the output voltage. This protects equipment and ensures consistent power, especially in systems with rectifiers.
- Inverter: It converts DC into AC. It is often used in renewable energy systems (such as solar power installations).
These components often work together in industrial setups. A transformer adjusts AC voltage. A rectifier changes it to DC. A regulator keeps the output steady. An inverter can turn DC back to AC if needed.
What are the different types of rectifiers used in industry?
Several types of rectifiers meet diverse industrial needs. Each is tailored for specific applications:
- MOS Rectifiers: They are very efficient with low power loss. This makes them ideal for energy-saving, high-power uses.
- Micro-Arc Oxidation Power Supplies: They offer precise control. They suit processes needing high-quality oxide coatings.
- Surface Treatment Rectifiers: They provide stable DC power for electroplating and anodizing. This ensures consistent results and high product quality.
Each type has a unique role. They help industries meet their tech needs and perform at their best.
What are the key factors when choosing a rectifier?
Choosing the right rectifier is essential for the success of your industrial processes. Key considerations include:
- Voltage and Current Requirements: Ensure compatibility with the specific needs of your application.
- Efficiency: High-efficiency rectifiers reduce energy consumption and operational costs.
- Compatibility: Make sure the rectifier works well with your systems. This includes CNC machines and electroplating equipment.
- Power Stability and Control: Precise tasks need advanced regulation. It’s key for micro-arc oxidation and surface treatments.
By considering these factors, you can choose a reliable rectifier. It will ensure efficiency and consistent performance in your operations.
In conclusion, rectifiers are essential in industrial power systems. They provide stable DC power for processes like electroplating, anodizing, and micro-arc oxidation. Knowing how rectifiers differ from transformers, regulators, and inverters helps improve power systems. Choosing the right rectifier boosts efficiency, reduces defects, and ensures success.
